Why Blockchain #1 - Integrating Crypto Rails into the Global Payment Network
We believe payments industry can greatly benefit from the adoption of blockchain technology.
漢文版本請點此連結
Special thanks to Jamie, Joseph, Jessica, Ching, Jack, Johnny, Donn for feedback and review and suggestions.
All too often, many projects in the crypto world find themselves getting caught up in the technical details of their projects, often losing the forest for the trees, and ultimately end up lacking a sufficient real-world use case. Essentially, “if all you have is a hammer, everything looks like a nail.”
To avoid this, we apply the "First Principle" approach, to look at problems from the user's point of view, and adopt blockchain when it's meaningfully 10x better than incumbent solutions. Framing it in this perspective, we believe that the payments industry can greatly benefit from the adoption of blockchain technology.
We've been talking for years about how blockchain can transform the payments industry. Since the release of the Bitcoin white paper, the subject has been brought up countless times. So, why haven't we seen widespread adoption yet? We will try to answer this question in the article.
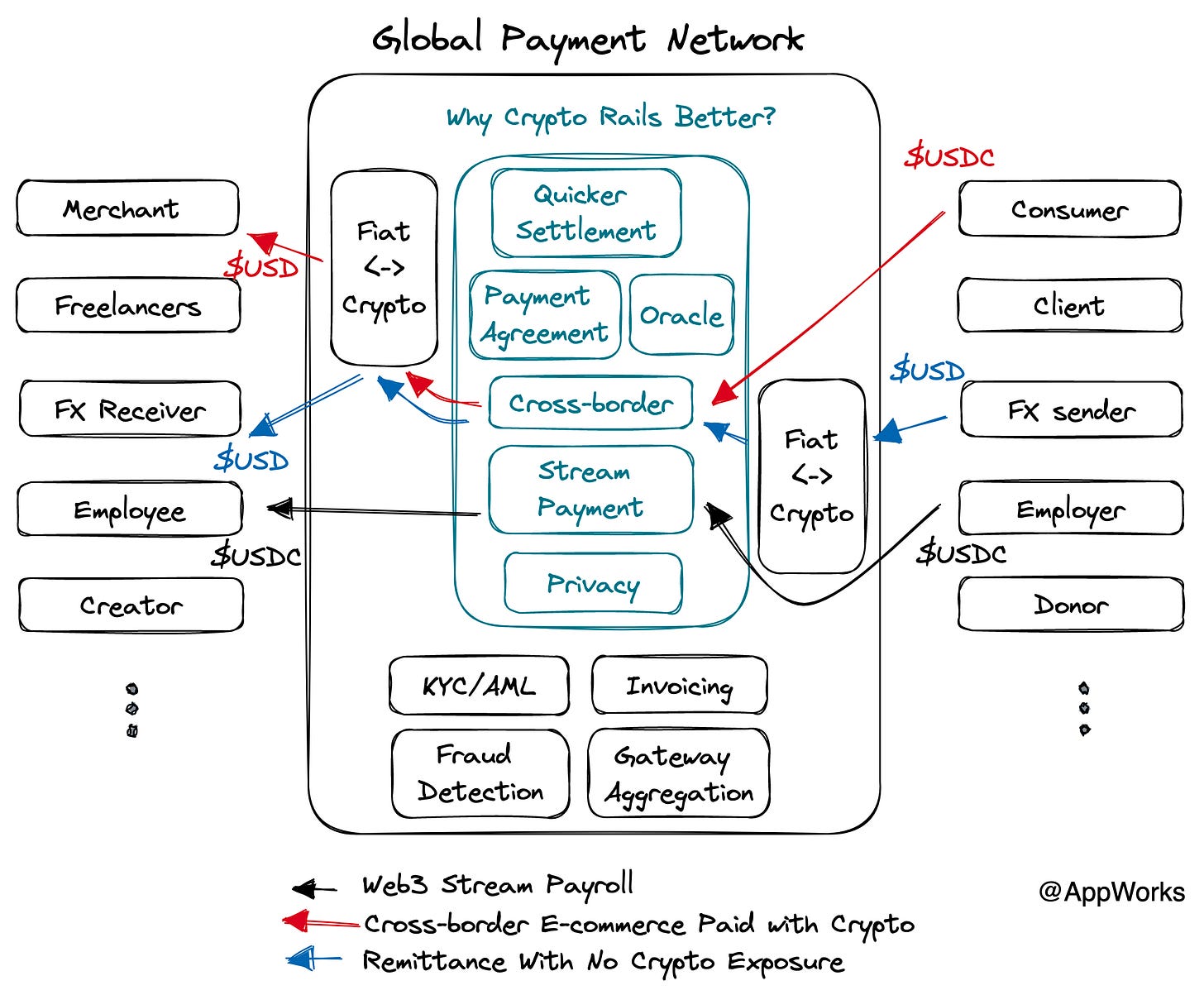
So why are crypto rails better?
Blockchain can facilitate instant settlements within seconds to minutes, depending on the chain's performance.
Thanks to instant settlement and low costs, Stream Payment can be achieved.
Blockchain transactions are not limited by geography.
Blockchain's smart contract feature enables programmable payments.
Next, let's delve into how these four features can solve problems ten times more efficiently than existing alternatives. Specifically, we're most optimistic about resolving the following three issues.
Problem 1: The SWIFT system is slow, expensive, and subject to geographical limitations
SWIFT links thousands of global financial institutions to transmit money transfer messages. However, SWIFT, a system from the 1970s, has many problems including slow speed, especially for international transactions which may take several business days to complete. SWIFT is also expensive, as more costs accumulate with each additional intermediary bank, each charging a fee of tens of dollars. Moreover, there are geographical limitations, with some regional banks still unable to connect to SWIFT.
In the short term, it seems unlikely that blockchain could completely replace the SWIFT system as this would require many financial institutions to adopt it. In 2020, J.P. Morgan launched blockchain network Onyx for interbank settlement, but progress has been slow as other banks have been hesitant to join, in part due to competitive reservations. Fully decentralized settlement networks (like BTC/ETH) would face substantial obstacles due to regulatory, compliance, and reporting system challenges.
I believe that for a global financial settlement network, it's more likely that Visa or Mastercard's Payment Processing Network will adopt it since credit card companies are private, international companies that already possess substantial network effects. In fact, Visa's head of cryptocurrency, Cuy Sheffield, stated in a forum in February 2023, "The current use of SWIFT restricts us from frequently moving funds due to many limitations in SWIFT. So, today I'm publicly announcing that Visa has been testing how to make settlements with the USDC stablecoin on the Ethereum blockchain."
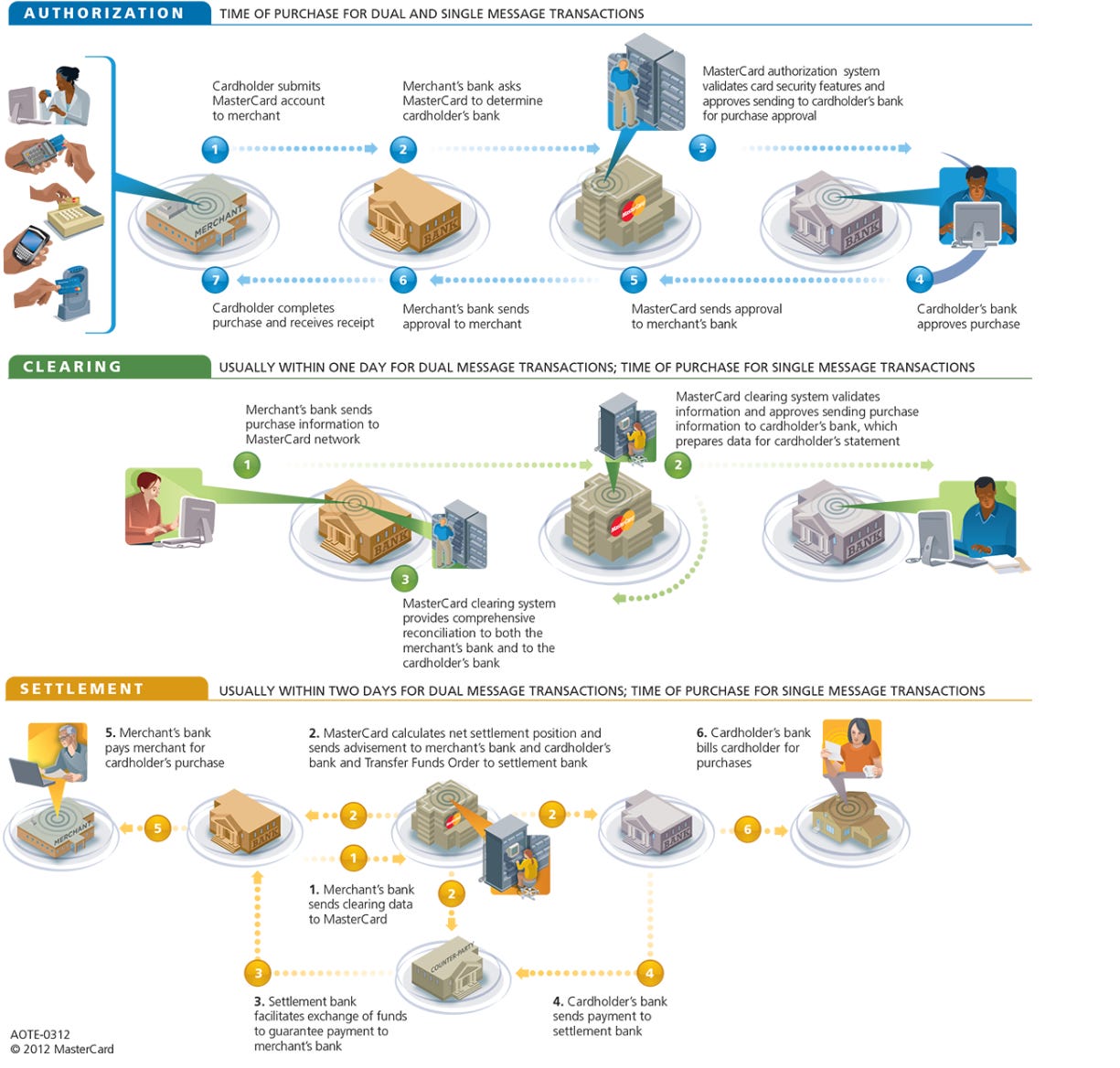
For reference, a credit card transaction goes through three stages:
Authorization: When a transaction occurs, the acquiring bank and the issuing bank need to verify the transaction through the credit card company. They ensure it's not a fraudulent activity or that the card isn't maxed out.
Clearing: The credit card company helps the issuing bank and the acquiring bank to reconcile the money flow, calculating who owes what to whom.
Settlement: Once this is figured out, the credit card company sends the information to a clearing bank, which transfers funds between the acquiring bank and the issuing bank.
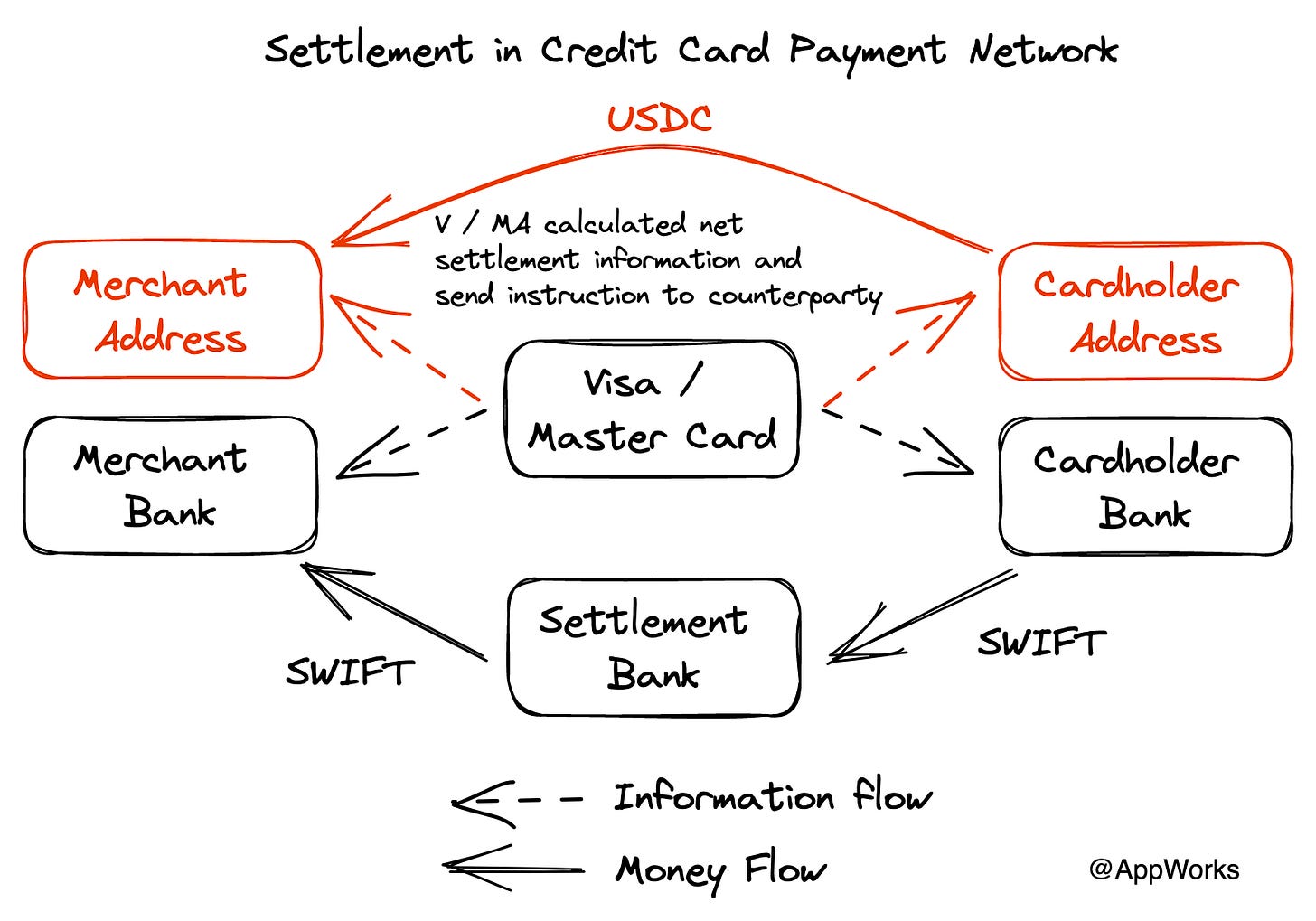
Visa is planning to use blockchain for the Settlement stage. Given the issues with SWIFT mentioned above, Visa is actively exploring how to use USDC for settlements to speed up the process, reduce costs, and particularly improve cross-border payments. For instance, currently, if you send US$100 from the United States to Europe via PayPal and convert it to Euros, the cost is US$7.75, which includes both domestic and international transfer fees (US$4.80) and currency exchange fees (US$2.95). In contrast, using USDC for settlement only incurs gas fees, which is around US$0.20 with Layer 2 solutions. As Ethereum continues to upgrade, the cost will be even lower. Although currency conversion costs still apply, the advantage in transfer fees is evident, not to mention the efficiency of settlements.
If Visa widely adopts blockchain as the settlement layer, the settlement parties could shift from 'issuing bank' and 'acquiring bank' to 'issuing address' and 'acquiring address.' This removes the need for a settlement bank, and the card issuing institution doesn't even need to be a traditional bank,eliminating the hassle of waiting for banks to accept stablecoins on their balance sheets, and ultimately accelerating card issuance. It also solves the off-ramp problem, making the flow of cryptocurrency more convenient. Visa's research in January 2023 on using 'Account Abstraction' to achieve 'Crypto Pull Payment' indicates their intention to directly use addresses or smart contracts for settlements. Pull Payment is similar to the mechanisms behind credit cards, but it's currently challenging to implement with existing blockchain infrastructure. However, the future may see solutions through account abstraction.
The real value of Visa and Mastercard lies in their ability to offer merchants and users fraud detection. They use information from banks, consumer and merchant locations, past transaction records, and amounts for risk scoring. If the risk is too high, they utilize 2FA/MFA verification.
So, what are the challenges Visa and Mastercard face before adopting stablecoins for settlement? I believe the following areas still need to be addressed:
Institutions willing to accept cryptocurrencies or stablecoins for card issuance, or web3 projects capable of risk management (wallets seem the most suitable), can incentivize Visa and Mastercard to issue more cards. Palladium, aiming to be a Crypto Native Neobank, and Stables, which recently partnered with Mastercard, are notable examples.
On-chain data fraudulent activities detection, providing risk control services for payment providers. Chainalysis and TRM Labs are more oriented towards AML, whereas payment networks require services designed to detect card theft. In the on-chain context, this means detecting stolen private keys or preventing fund transfers to suspicious addresses by triggering 2FA or MFA verification. For example, Sardine detects crypto and NFT fraud and provides risk control services for payment companies. Chainsight, a Taiwanese project selected by YC, is also working in this field.
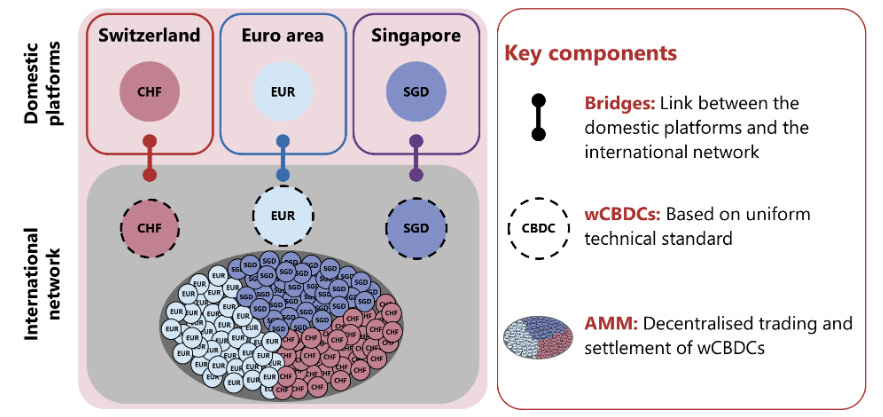
Liquidity of stablecoins, US dollars, and local currencies. Visa and Mastercard should have no problem obtaining liquidity for USDC and dollars from Circle, but the liquidity between USDC and other local currencies is another problem. If liquidity is insufficient, slippage increases and costs rise. Of course, people could first exchange for USD before converting to other local currencies, but this again involves traditional financial institutions. Another approach is direct exchange between local currencies and USDC, or each local currency could have on-chain direct blockchain settlement, while on-chain local currency liquidity could potentially be provided through DeFi. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS), often referred to as the "central bank of central banks," is working on Project Mariana, which shares similar concepts. The project shows how EUR, CHF, and SGD provide liquidity through an AMM model.
Problem 2: High dispute incidence and management cost in Payment Agreements.
As the post-pandemic era and the age of AI assistance arrive, the gig economy is maturing, and the freelance market is expected to continue its rapid growth. Freelancers and employers will adopt various payment agreements to establish clear payment terms, avoid payment disputes, and protect the rights of both parties. As a result, the types of payment agreements on the market have become more prevalent, including escrowed payment, milestone payment, recurring payment, etc. Not only freelance platforms, but other services including e-commerce platforms, DAO/web3 business's community contribution compensation, gifting, etc., will also make extensive use of payment agreements.
There are several problems with current Payment Agreements, such as:
Unclear agreements, leading to 64% of freelancers having payment delays due to disputes.
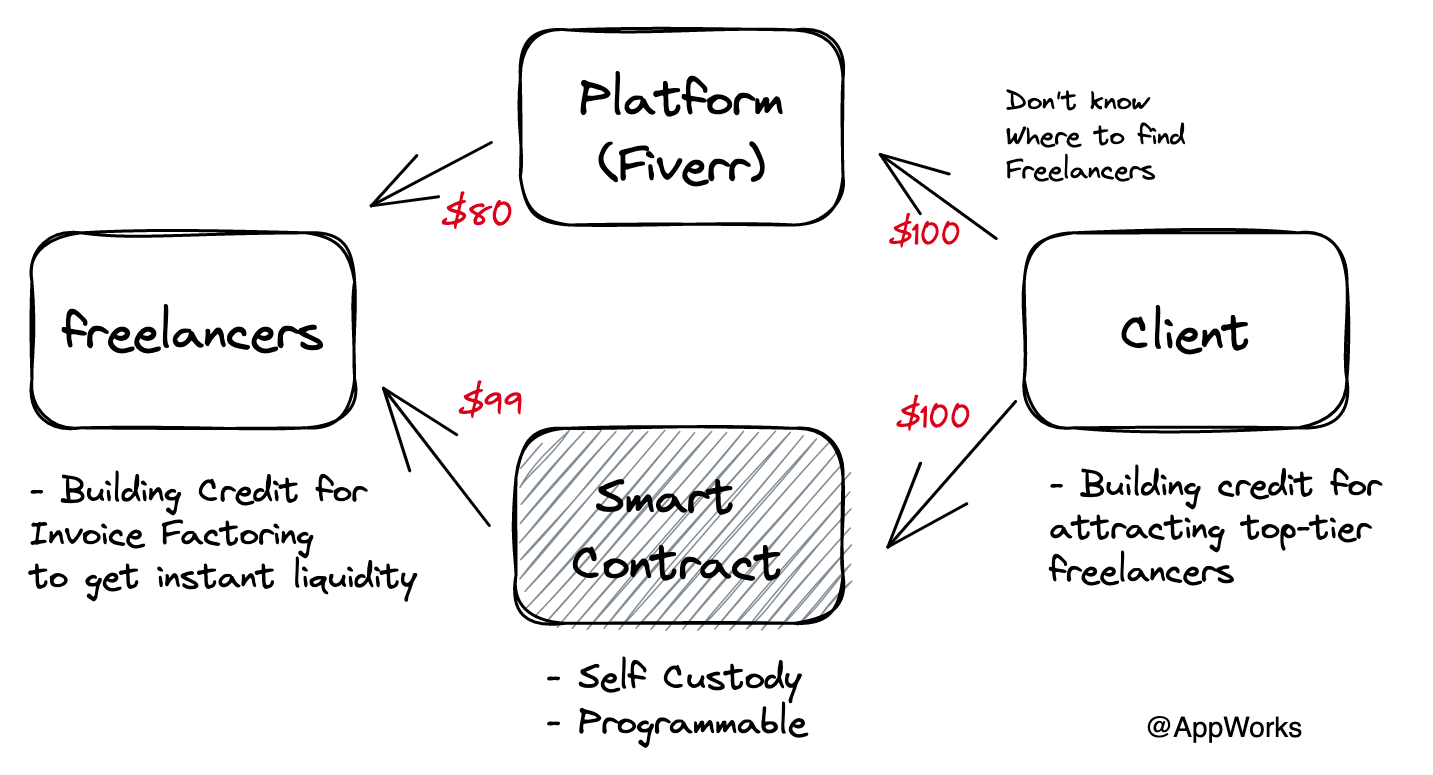
In addition to the platform's service fee of 5-20%, freelancer platforms also charge an additional payment processing fee of 2.5-5%, which is quite high.
Freelancers outside the platform often encounter scams and non-payment by clients.
However, if the terms are written into a smart contract, the conditions of the payment agreement can be triggered more promptly. If it's possible to fully integrate multiple oracles for acceptance verification, it may even achieve automated milestone payment. For instance, utilizing numbers like the total value locked (TVL) growth rate for immediate performance payment could reduce the delay in freelancers' payment collection. Using blockchain as a settlement tool for payment, or escrowing funds within a smart contract, can reduce payment processing costs.
Invoices generated by blockchain settlement can also be minted into NFTs, serving as a source of on-chain credit data. The decentralized nature of NFTs means that they are not tied to a specific platform and can be more freely linked to any freelancer platform, or even social media platform. Once the credit system is established, the freely circulable feature of NFTs can even be used for invoice factoring business.
Blockchain can reduce the cost of payment agreements, lower execution cost and escrow fees through smart contracts, and even improve execution efficiency through automatic execution via oracles. In addition, blockchain can create a portable reputation system for freelancers that is closely linked to financial information and business information, and this data can be utilized for financial services in the future.
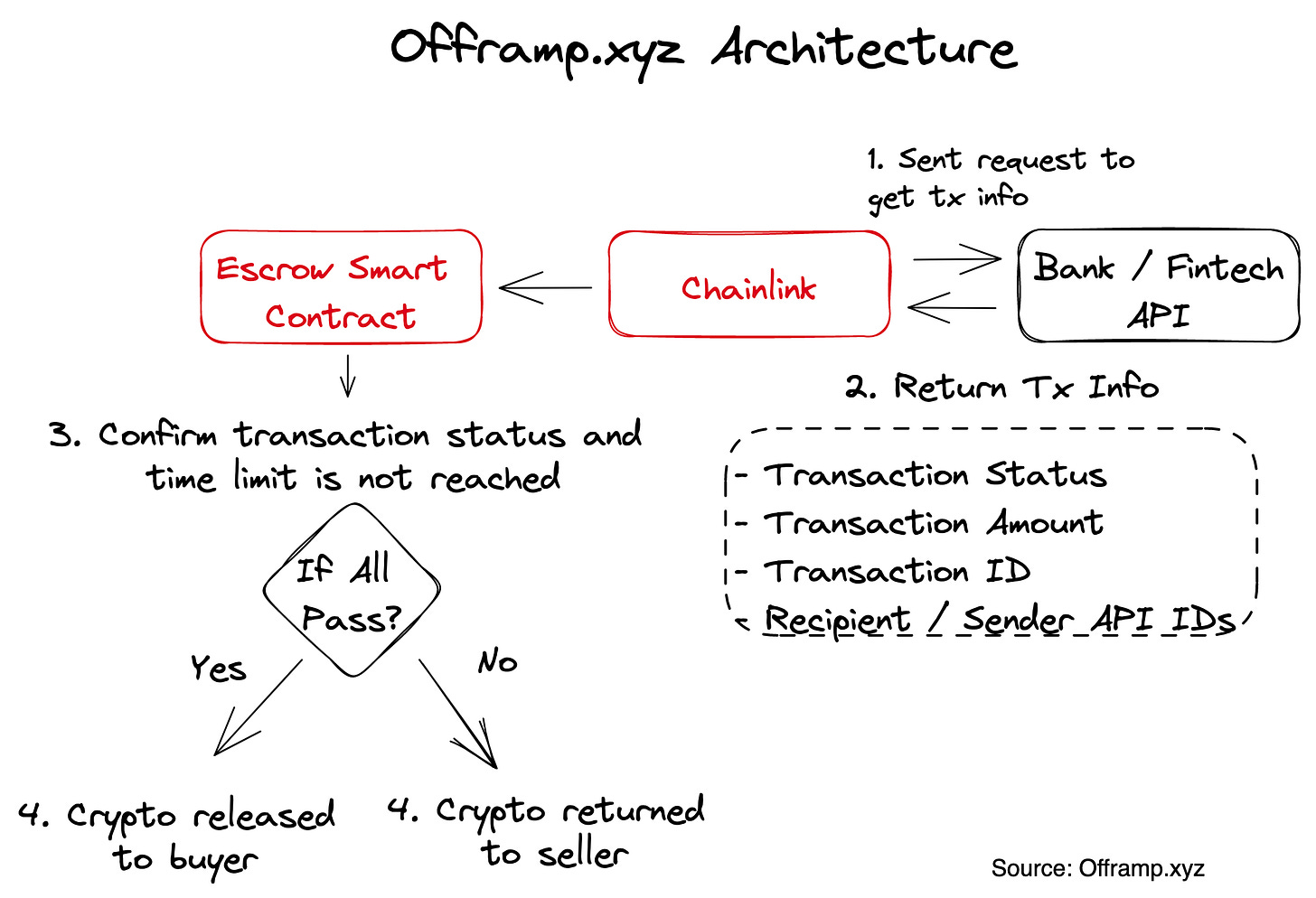
Beyond freelancers, we have also observed a convenient off-ramp platform, which integrates web2 data, connects Chainlink API to pass data onto the chain, and triggers the conditions of an escrowed smart contract. As shown below, Offramp.xyz connects with international money transfer service provider WISE's API to confirm the arrival of fiat currency, then uses Chainlink to transmit data onto the chain. If the transaction data matches, the smart contract automatically completes the payment. The overall withdrawal process only takes 20 seconds, providing a smooth experience, and demonstrating the value of combining smart contracts and oracles to make payment agreements. In the future, if more banking and fintech APIs can be connected, liquidity will greatly increase through network effects
However, there are still some unresolved issues:
How can we trigger offline conditions to accomplish more complex payment agreements? In addition to token prices, Chainlink also provides data feeds for weather, athletes, supply chains, IoT, and customizable feeds for businesses. Offramp.xyz has successfully utilized WISE's data to create a convenient off-ramp platform, but it is limited to users of WISE. If we could access banking APIs or a future universal open banking API, we would be able to expand the range of these payment agreement applications.
Dispute resolution: If the platform automatically executes payments, it implies that the platform bears the risk of the verifier, and creates conditions for complications. Therefore, dispute resolution service providers such as Kleros become important as they act as independent judiciaries to assist platforms in resolving disputes. In addition, with the accumulation of oracle data and improved reliability of data sources, milestones can be defined in broader and clearer terms naturally reducing the chances of disputes. Moreover, credit building is also one of the ways to reduce the risk of disputes.
Problem 3: High costs and complex administrative processes for recurring payments
According to data from Stripe, about 18% of global online transactions are recurring payments. Scenarios that use recurring payments include subscriptions, payroll, supplier payments (accounts receivable/accounts payable), etc. However, there are several issues with current recurring payments:
The interval flexibility of recurring payments is not sufficient, sometimes causing cash flow issues for employees and suppliers, and generating additional borrowing costs.
Most of the infrastructure for recurring payments online is built upon the credit card network, which incurs costs amounting to 2-3% of the total transaction volume.
Crypto payments can capitalize on its fast and inexpensive settlement system to execute stream payments, which enables businesses, employees, suppliers, and investors to receive funds or tokens within seconds. This accelerates the speed of fund circulation and improves cash flow for businesses and individuals.
Yet, generally, payers want to delay payments as long as possible, while the receiver prefers to receive payment as soon as possible. There is a conflict of interest here, and therefore, stream payment is not necessarily better than existing solutions. However, in certain specific use cases, it can offer greater payment flexibility:
Simplifying corporate finance operations: Many crypto companies/DAOs use services like Request or Zebec to pay their employees or contributors per second with stream payments, thereby eliminating the need for monthly administrative procedures.
Instant paycheck for people who live paycheck to paycheck: Stream payment of wages can reduce the need to borrow money from financial institutions. In the US, one-fifth of the working class borrows money from payday loan institutions before the next paycheck, where the average interest rate is a whopping 200-700%. Stream payment of wages can potentially reduce the demand for payday loans or at least cut down on bank overdraft fees. An economic report issued by the White House also stated that implementing a faster bank settlement system could save low-income households US$7 billion annually.
Provide shorter-term subscription services, reduce the period from monthly to per second, and improve conversion rates. Offering a variety of pricing options and different subscription periods can meet a broader range of customer needs and budgets. Shorter subscription periods may make customers more willing to try out a product or service.
Stream token vesting allows investors to receive released tokens every second, reducing one-time selling pressure on tokens and potentially decreasing liquidity management costs for crypto projects.
It must be said that most of the use cases mentioned above are limited, or the additional benefits are not very obvious. Stream payment is more a "nice-to-have" feature, which cannot attract a material number of new customers or merchants. Only by integrating more features can a 10x better product be made to achieve mass adoption.
But we still want to highlight one thing, most web2 services utilize a pull payment method, such as credit cards, where the payee needs the payer's authorization to "pull" funds from their bank account. This process requires several steps to verify the reliability of the authorization, such as 2FA and MFA mechanisms, and also generates many additional transaction fees. However, crypto can conveniently implement a push payment method to execute recurring payments. When widely adopted, it can even bypass the Visa and Mastercard payment networks, avoiding a 2-3% transaction fee. Looking broadly, the market opportunity of 2-3% of 18% of global online transaction amounts is substantial.
Conclusion: Integrating Crypto Rails into the global payment network
Crypto rails demonstrate clear advantages, such as fast settlement speed, payment agreements that automatically execute based on complex conditions, a settlement network that is not restricted by national boundaries, cheaper micropayments, and even stream payments. But these benefits won't lead to mass adoption.
The key is to deeply understand the needs of different payers and payees. There are countless types of payers and payees, and we need to ask: which needs are not currently met by the existing payment network? For example, stream payment can reduce the demand for payday loans, the costs of cross-border e-commerce and remittances can be lowered, milestone payments between platforms and freelancers can be more easily executed, investors can more efficiently execute trading strategies through stream payments, and banks can settle faster through crypto rails.
However, these are all individual breakthroughs. The payment industry is already quite mature. In order to compete with traditional payment industry players, apart from offering the advantages of crypto rails, it is also necessary to provide existing services such as anti-money laundering, fraud detection, and invoice management services to attract more customers. Moreover, it is worth considering whether it's possible to leverage on-chain data to create better or even completely new services, such as on-chain fraud detection, comprehensive credit data established through on-chain invoice information, privacy payments using ZK technology, and so on. Only then is there a chance to create a product that is 10x better, truly addressing people's pain points and ultimately achieving mass adoption.
If you are an entrepreneur striving in this field and believe that blockchain technology can solve problems in the payment industry, feel free to contact AppWorks! If any industry veterans have additional thoughts or different opinions, you are also very welcome to leave comments for discussion!